Bayesian Hierarchical Modeling and its Applications
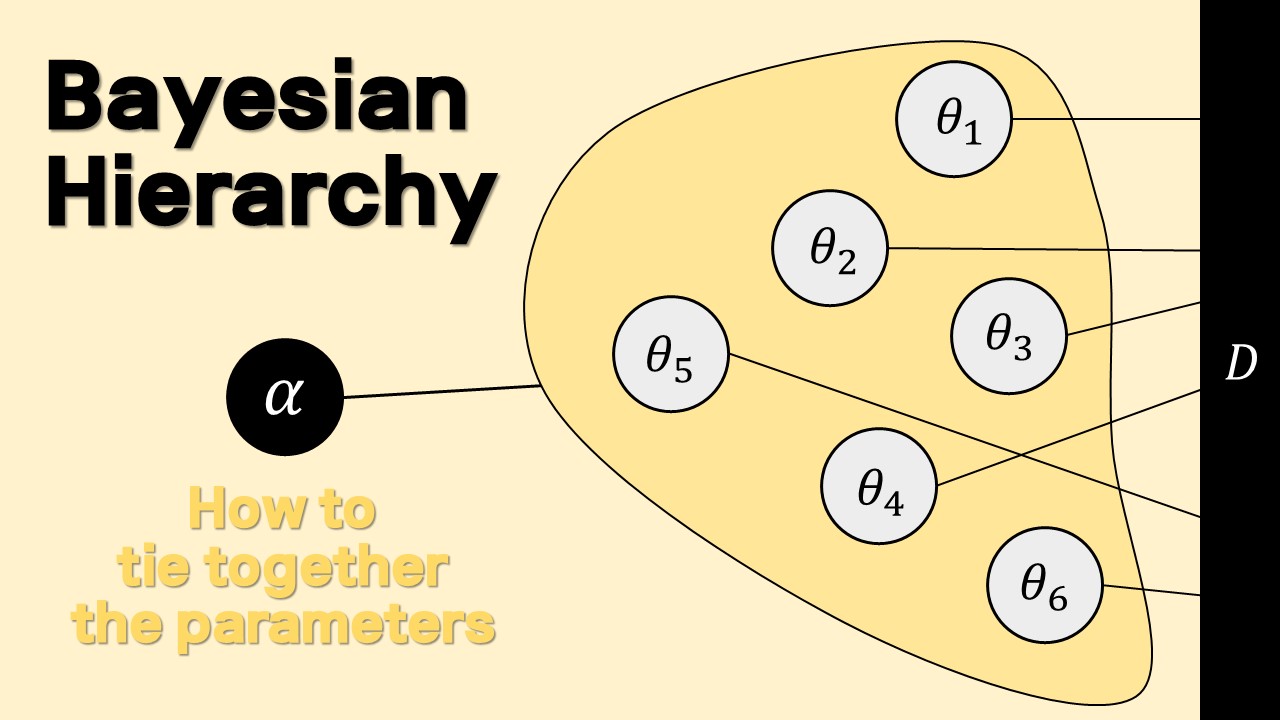
여러 모수를 한 묶음으로 묶어주는 Hyperparameter
Review: Full conditional posterior for normal likelihood 일단 정규분포의 semi-conjugate prior에 대한 내용을 다시 정리해보자.
$p(\theta\mid\sigma^2, \mathbf{D}) = dnorm(\theta, \mu_n, \tau_n^2)$ $\mu_n= \dfrac{1/\tau_0^2}{\frac{1}{\tau_0^2} + \frac{n}{\sigma^2}}\mu_0 + \dfrac{\frac{n}{\sigma^2}}{\frac{1}{\tau_0^2} + \frac{n}{\sigma^2}}\bar{x}$ $\tau_n^2 = \dfrac{1}{\frac{1}{\tau_0^2} + \frac{n}{\sigma^2}}$ $p(\sigma^2\mid\theta, \mathbf{D}) = dinv\Gamma(\sigma^2, v_n, \dfrac{1}{v_n}(v_0\sigma_0^2+\sum (y_i-\theta)^2)$ Two Group Comparison: Math scores library(ggplot2) library(cowplot) school1 = dget('http://www2.stat.duke.edu/~pdh10/FCBS/Inline/y.school1') school2 = dget('http://www2.stat.duke.edu/~pdh10/FCBS/Inline/y.school2') df = data.frame(school = c(rep('s1', length(school1)),rep('s2', length(school2))), score = c(school1, school2) ) ggplot(df, aes(x=school, y=score))+ geom_boxplot(aes(fill=school))+ ggtitle('Math scores comparison')+ theme_cowplot() 통계학이 필요한 이유는 이런 “애매한” 차이 때문이다.
